The remainder of this Chapter consists of a brief reference guide to Q-Chem’s built-in ECPs. The ECPs vary in their complexity and their accuracy and the purpose of the guide is to enable the user quickly and easily to decide which ECP to use in a planned calculation.
The following information is provided for each ECP:
The elements for which the ECP is available in Q-Chem. This is shown on a schematic Periodic Table by shading all the elements that are not supported.
The literature reference for each element for which the ECP is available in Q-Chem.
The matching orbital basis set that Q-Chem will use for light (i.e.. non-ECP atoms). For example, if the user requests SRSC ECPs—which are defined only for atoms beyond argon—Q-Chem will use the 6-311G basis set for all atoms up to Ar.
The core electrons that are replaced by the ECP. For example, in the fit-LANL2DZ ECP for the Fe atom, the core is [Ne], indicating that the , and electrons are removed.
The maximum spherical harmonic projection operator that is used for each element. This often, but not always, corresponds to the maximum orbital angular momentum of the core electrons that have been replaced by the ECP. For example, in the fit-LANL2DZ ECP for the Fe atom, the maximum projector is of -type.
The number of valence basis functions of each angular momentum type that are present in the matching orbital basis set. For example, in the matching basis for the fit-LANL2DZ ECP for the Fe atom, there the three shells, three shells and two shells. This basis is therefore almost of triple-split valence quality.
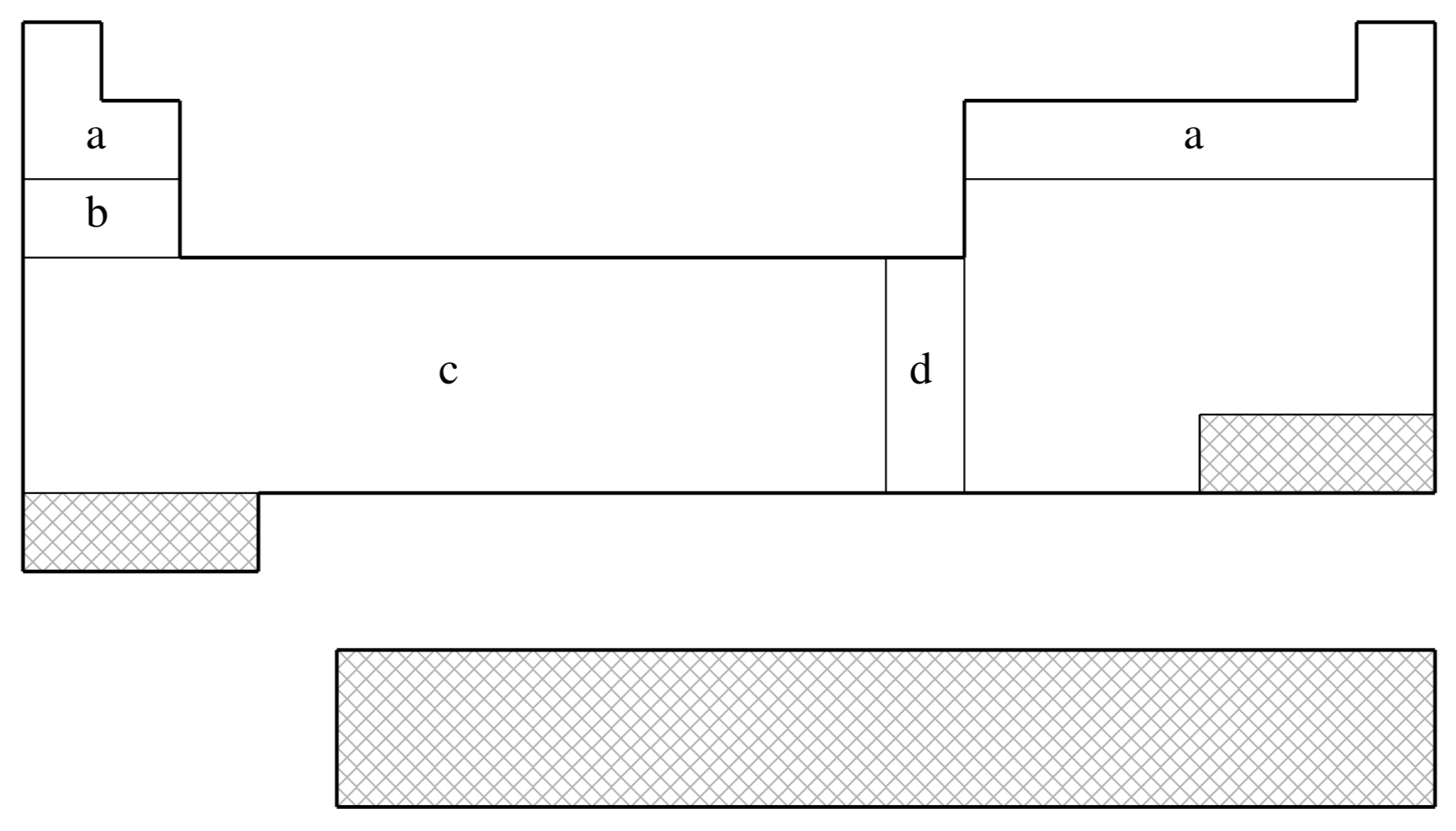
fit-HWMB is not available for shaded elements
| (a) | No ECP; Pople STO-3G basis used |
|---|---|
| (b) | Wadt & Hay (Ref.
1372
J. Chem. Phys. (1985), 82, pp. 284. Link ) |
| (c) | Hay & Wadt (Ref.
519
J. Chem. Phys. (1985), 82, pp. 299. Link ) |
| (d) | Hay & Wadt (Ref.
518
J. Chem. Phys. (1985), 82, pp. 270. Link ) |
| Element | Core | Max Projector | Valence |
|---|---|---|---|
| H–He | none | none | (1s) |
| Li–Ne | none | none | (2s,1p) |
| Na–Ar | [Ne] | (1s,1p) | |
| K–Ca | [Ne] | (2s,1p) | |
| Sc–Cu | [Ne] | (2s,1p,1d) | |
| Zn | [Ar] | (1s,1p,1d) | |
| Ga–Kr | [Ar]+3d | (1s,1p) | |
| Rb–Sr | [Ar]+3d | (2s,1p) | |
| Y–Ag | [Ar]+3d | (2s,1p,1d) | |
| Cd | [Kr] | (1s,1p,1d) | |
| In–Xe | [Kr]+4d | (1s,1p) | |
| Cs–Ba | [Kr]+4d | (2s,1p) | |
| La | [Kr]+4d | (2s,1p,1d) | |
| Hf–Au | [Kr]+4d+4f | (2s,1p,1d) | |
| Hg | [Xe]+4f | (1s,1p,1d) | |
| Tl–Bi | [Xe]+4f+5d | (1s,1p) |
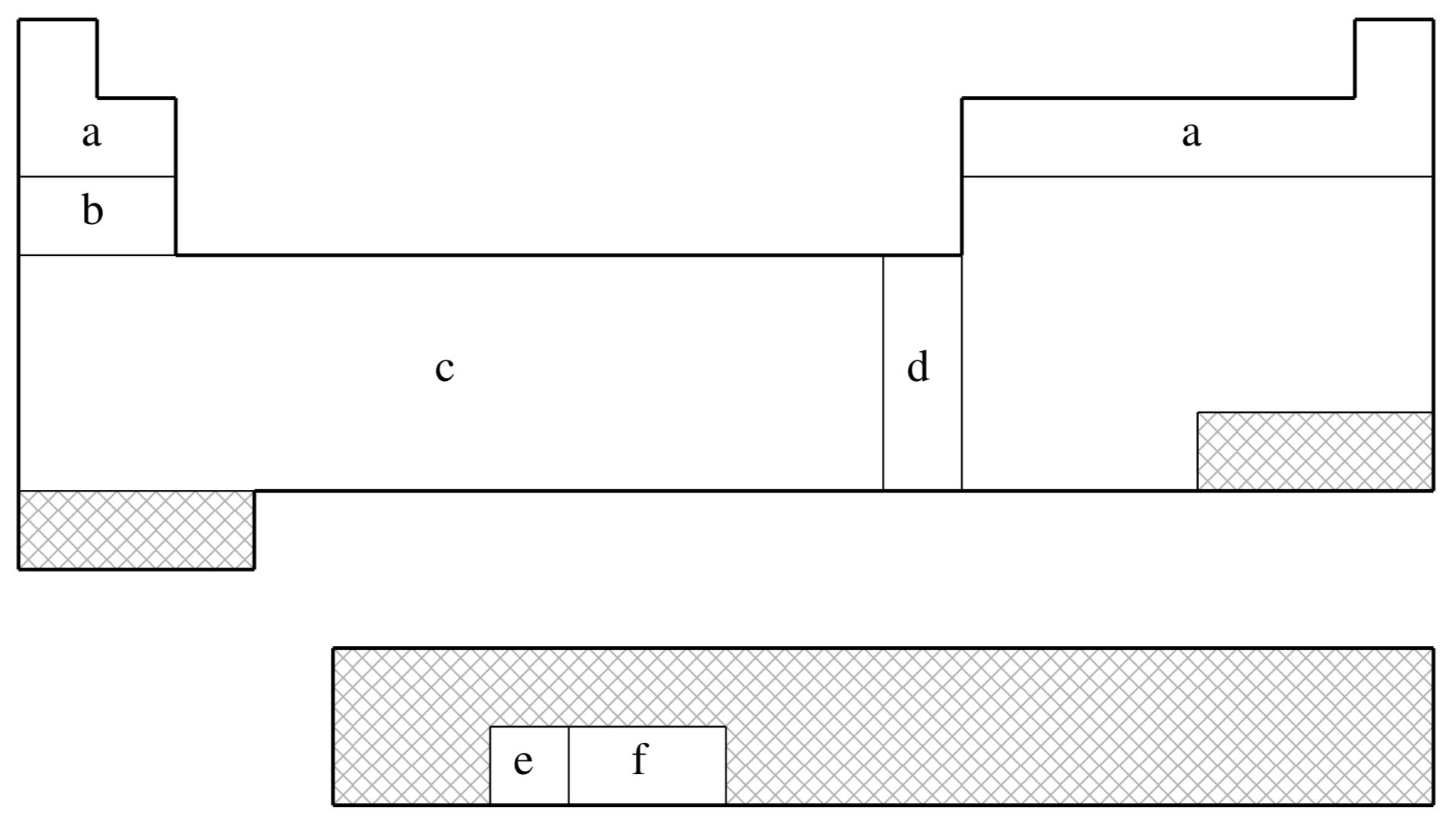
fit-LANL2DZ is not available for shaded elements
| (a) | No ECP; Pople 6-31G basis used |
|---|---|
| (b) | Wadt & Hay (Ref.
1372
J. Chem. Phys. (1985), 82, pp. 284. Link ) |
| (c) | Hay & Wadt (Ref.
519
J. Chem. Phys. (1985), 82, pp. 299. Link ) |
| (d) | Hay & Wadt (Ref.
518
J. Chem. Phys. (1985), 82, pp. 270. Link ) |
| (e) | Hay (Ref.
520
J. Chem. Phys. (1983), 79, pp. 5469. Link ) |
| (f) | Hay & Martin (Ref.
517
J. Chem. Phys. (1998), 109, pp. 3875. Link ) |
| Element | Core | Max Projector | Valence |
|---|---|---|---|
| H–He | none | none | (2s) |
| Li–Ne | none | none | (3s,2p) |
| Na–Ar | [Ne] | (2s,2p) | |
| K–Ca | [Ne] | (3s,3p) | |
| Sc–Cu | [Ne] | (3s,3p,2d) | |
| Zn | [Ar] | (2s,2p,2d) | |
| Ga–Kr | [Ar]+3d | (2s,2p) | |
| Rb–Sr | [Ar]+3d | (3s,3p) | |
| Y–Ag | [Ar]+3d | (3s,3p,2d) | |
| Cd | [Kr] | (2s,2p,2d) | |
| In–Xe | [Kr]+4d | (2s,2p) | |
| Cs–Ba | [Kr]+4d | (3s,3p) | |
| La | [Kr]+4d | (3s,3p,2d) | |
| Hf–Au | [Kr]+4d+4f | (3s,3p,2d) | |
| Hg | [Xe]+4f | (2s,2p,2d) | |
| Tl | [Xe]+4f+5d | (2s,2p,2d) | |
| Pb–Bi | [Xe]+4f+5d | (2s,2p) | |
| U–Pu | [Xe]+4f+5d | (3s,3p,2d,2f) |
Note that Q-Chem 4.2.2 and later versions also support the LANL2DZ-SV basis, which employs SV basis functions (instead of 6-31G) on H, Li-Ne elements (like some other quantum chemistry packages).
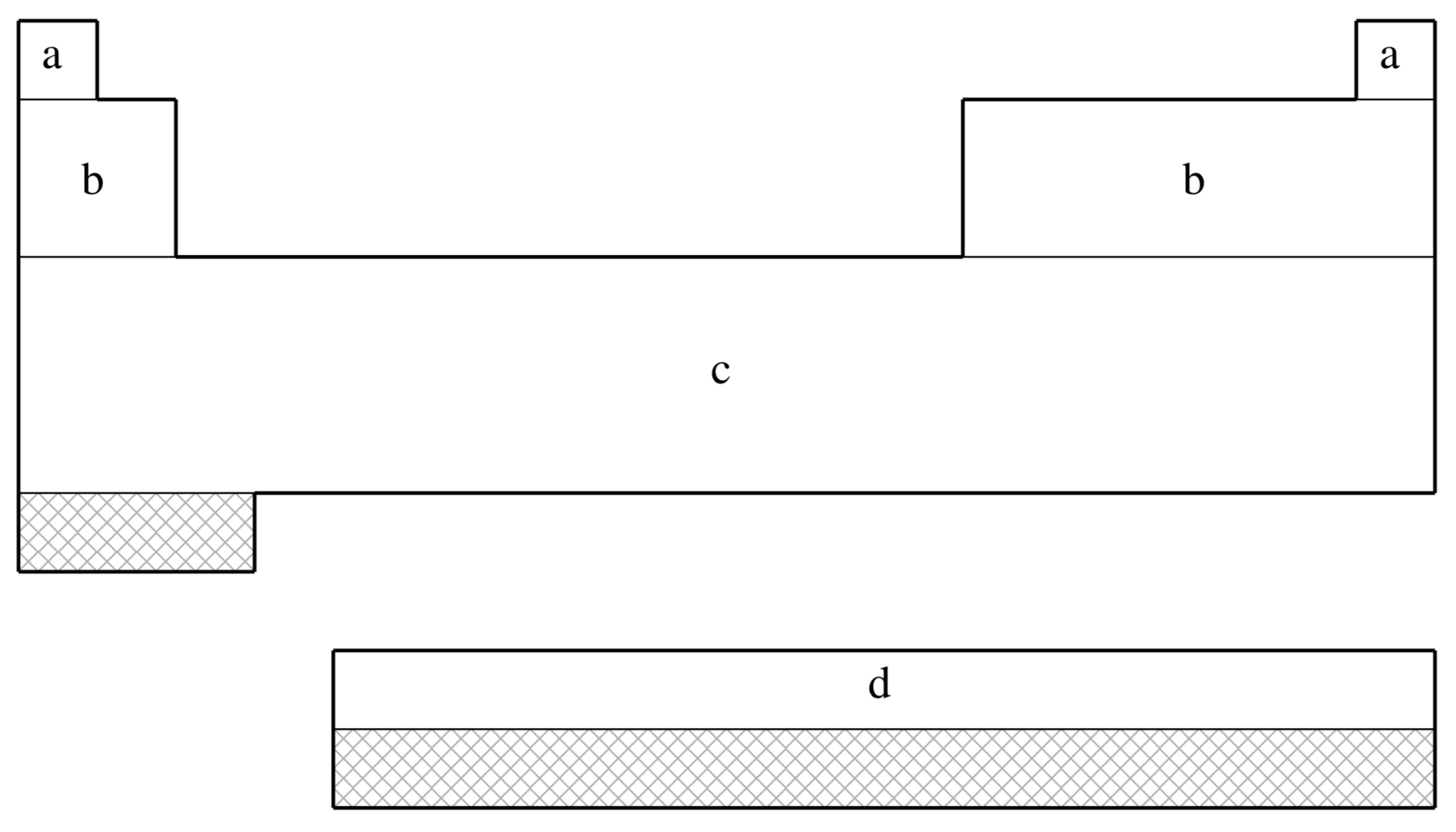
fit-SBKJC is not available for shaded elements
| (a) | No ECP; Pople 3-21G basis used |
|---|---|
| (b) | Stevens, Basch, & M. Krauss (Ref.
1267
J. Chem. Phys. (1984), 81, pp. 6026. Link ) |
| (c) | Stevens, Krauss, Basch, & Jasien (Ref.
1268
Can. J. Chem. (1992), 70, pp. 612. Link ) |
| (d) | Cundari & Stevens (Ref.
286
J. Chem. Phys. (1993), 98, pp. 5555. Link ) |
| Element | Core | Max Projector | Valence |
|---|---|---|---|
| H–He | none | none | (2s) |
| Li–Ne | [He] | (2s,2p) | |
| Na–Ar | [Ne] | (2s,2p) | |
| K–Ca | [Ar] | (2s,2p) | |
| Sc–Ga | [Ne] | (4s,4p,3d) | |
| Ge–Kr | [Ar]+3d | (2s,2p) | |
| Rb–Sr | [Kr] | (2s,2p) | |
| Y–In | [Ar]+3d | (4s,4p,3d) | |
| Sn–Xe | [Kr]+4d | (2s,2p) | |
| Cs–Ba | [Xe] | (2s,2p) | |
| La | [Kr]+4d | (4s,4p,3d) | |
| Ce–Lu | [Kr]+4d | (4s,4p,1d,1f) | |
| Hf–Tl | [Kr]+4d+4f | (4s,4p,3d) | |
| Pb–Rn | [Xe]+4f+5d | (2s,2p) |
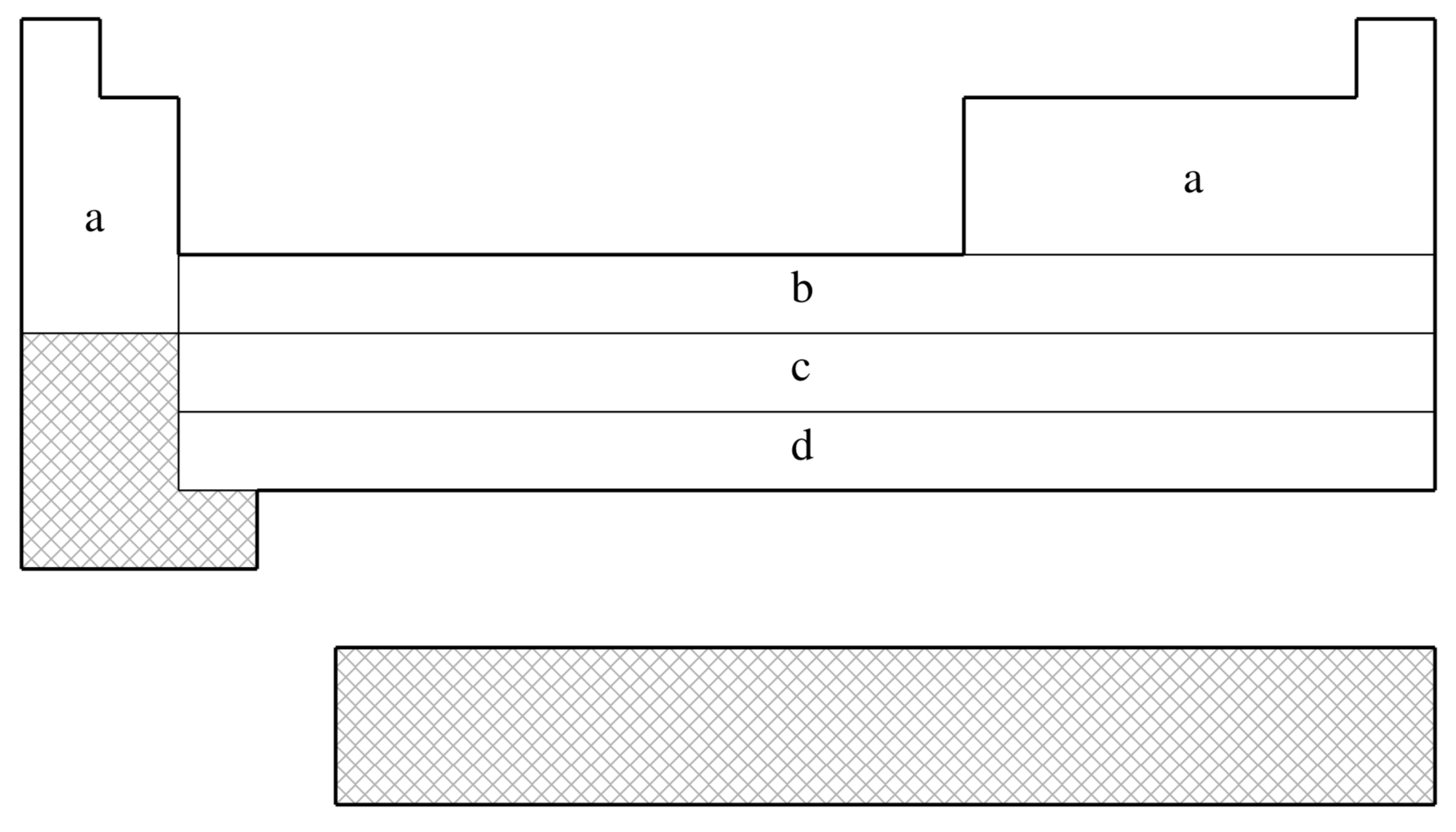
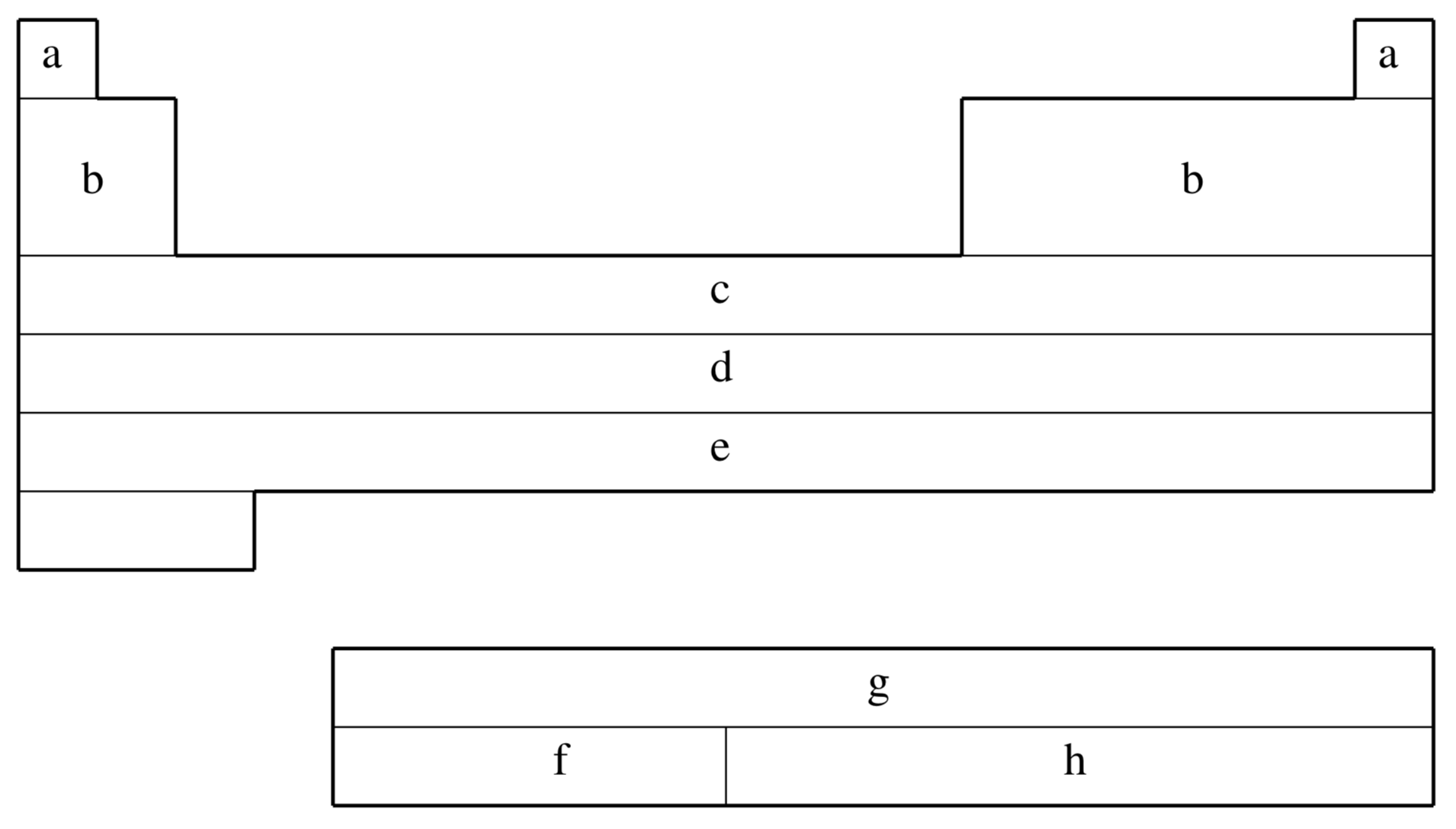
fit-CRENBS is not available for shaded elements
| (a) | No ECP; Pople STO-3G basis used |
|---|---|
| (b) | Hurley, Pacios, Christiansen, Ross, & Ermler (Ref.
591
J. Chem. Phys. (1986), 84, pp. 6840. Link ) |
| (c) | LaJohn, Christiansen, Ross, Atashroo & Ermler (Ref.
728
J. Chem. Phys. (1987), 87, pp. 2812. Link ) |
| (d) | Ross, Powers, Atashroo, Ermler, LaJohn & Christiansen (Ref.
1146
J. Chem. Phys. (1990), 93, pp. 6654. Link ) |
| (e) | Nash, Bursten, & Ermler (Ref.
953
J. Chem. Phys. (1997), 106, pp. 5133. Link ) |
| Element | Core | Max Projector | Valence |
|---|---|---|---|
| H–He | none | none | (1s) |
| Li–Ne | none | none | (2s,1p) |
| Na–Ar | none | none | (3s,2p) |
| K–Ca | none | none | (4s,3p) |
| Sc–Zn | [Ar] | (1s,0p,1d) | |
| Ga–Kr | [Ar]+3d | (1s,1p) | |
| Y–Cd | [Kr] | (1s,1p,1d) | |
| In–Xe | [Kr]+4d | (1s,1p) | |
| La | [Xe] | (1s,1p,1d) | |
| Hf–Hg | [Xe]+4f | (1s,1p,1d) | |
| Tl–Rn | [Xe]+4f+5d | (1s,1p) |
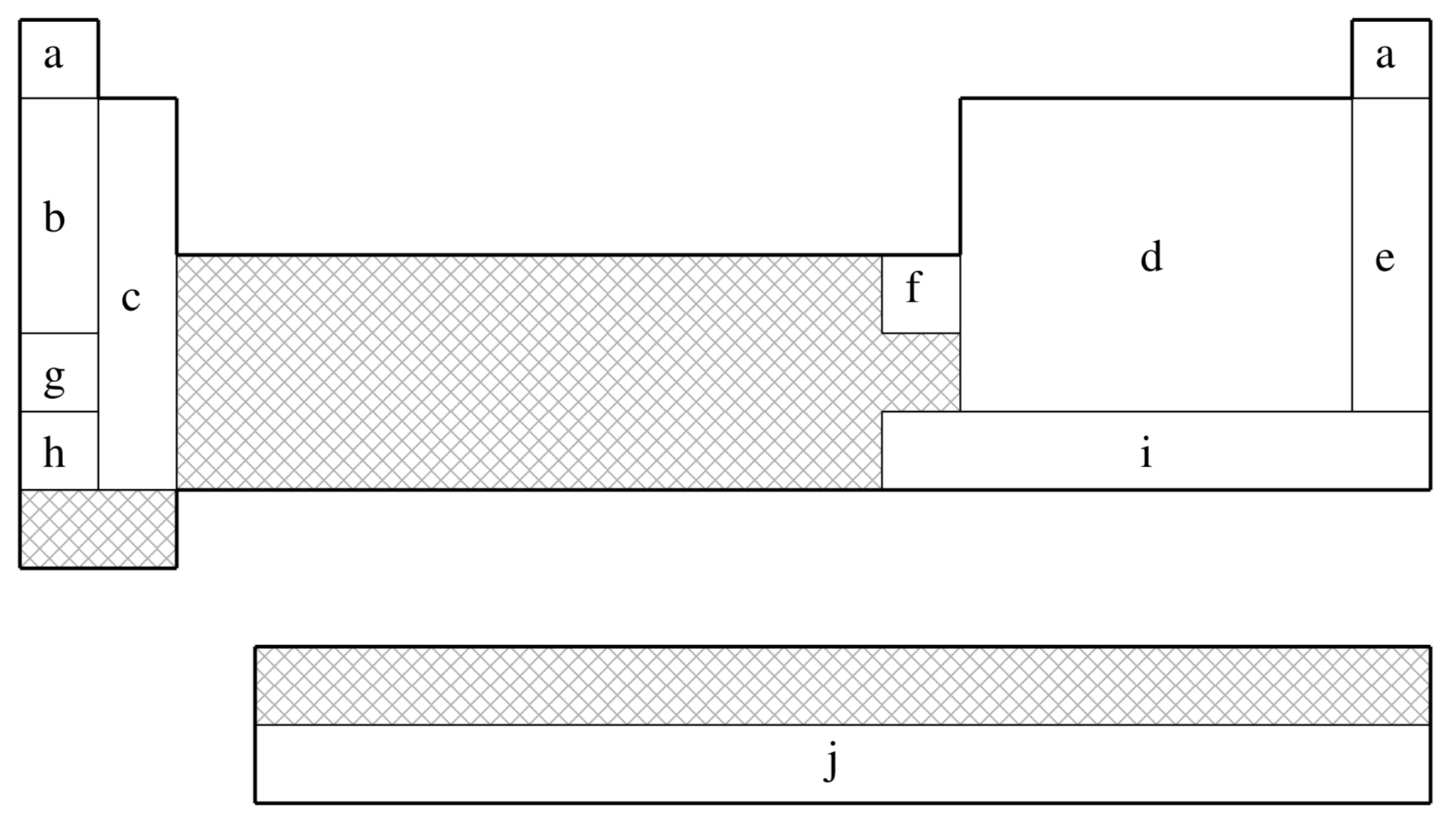
| (a) | No ECP; Pople 6-311G basis used |
|---|---|
| (b) | Pacios & Christiansen (Ref.
998
J. Chem. Phys. (1985), 82, pp. 2664. Link ) |
| (c) | Hurley, Pacios, Christiansen, Ross, & Ermler (Ref.
591
J. Chem. Phys. (1986), 84, pp. 6840. Link ) |
| (d) | LaJohn, Christiansen, Ross, Atashroo, & Ermler (Ref.
728
J. Chem. Phys. (1987), 87, pp. 2812. Link ) |
| (e) | Ross, Powers, Atashroo, Ermler, LaJohn, & Christiansen (Ref.
1146
J. Chem. Phys. (1990), 93, pp. 6654. Link ) |
| (f) | Ermler, Ross, & Christiansen (Ref.
362
Int. J. Quantum Chem. (1991), 40, pp. 829. Link ) |
| (g) | Ross, Gayen, & Ermler (Ref.
1145
J. Chem. Phys. (1994), 100, pp. 8145. Link ) |
| (h) | Nash, Bursten, & Ermler (Ref.
953
J. Chem. Phys. (1997), 106, pp. 5133. Link ) |
| Element | Core | Max Projector | Valence |
|---|---|---|---|
| H–He | none | none | (3s) |
| Li–Ne | [He] | S | (4s,4p) |
| Na–Mg | [He] | S | (6s,4p) |
| Al–Ar | [Ne] | P | (4s,4p) |
| K–Ca | [Ne] | P | (5s,4p) |
| Sc–Zn | [Ne] | P | (7s,6p,6d) |
| Ga–Kr | [Ar] | P | (3s,3p,4d) |
| Rb–Sr | [Ar]+3d | D | (5s,5p) |
| Y–Cd | [Ar]+3d | D | (5s,5p,4d) |
| In–Xe | [Kr] | D | (3s,3p,4d) |
| Cs–La | [Kr]+4d | D | (5s,5p,4d) |
| Ce–Lu | [Xe] | D | (6s,6p,6d,6f) |
| Hf–Hg | [Kr]+4d+4f | F | (5s,5p,4d) |
| Tl–Rn | [Xe]+4f | F | (3s,3p,4d) |
| Fr–Ra | [Xe]+4f+5d | F | (5s,5p,4d) |
| Ac–Pu | [Xe]+4f+5d | F | (5s,5p,4d,4f) |
| Am–Lr | [Xe]+4f+5d | F | (0s,2p,6d,5f) |
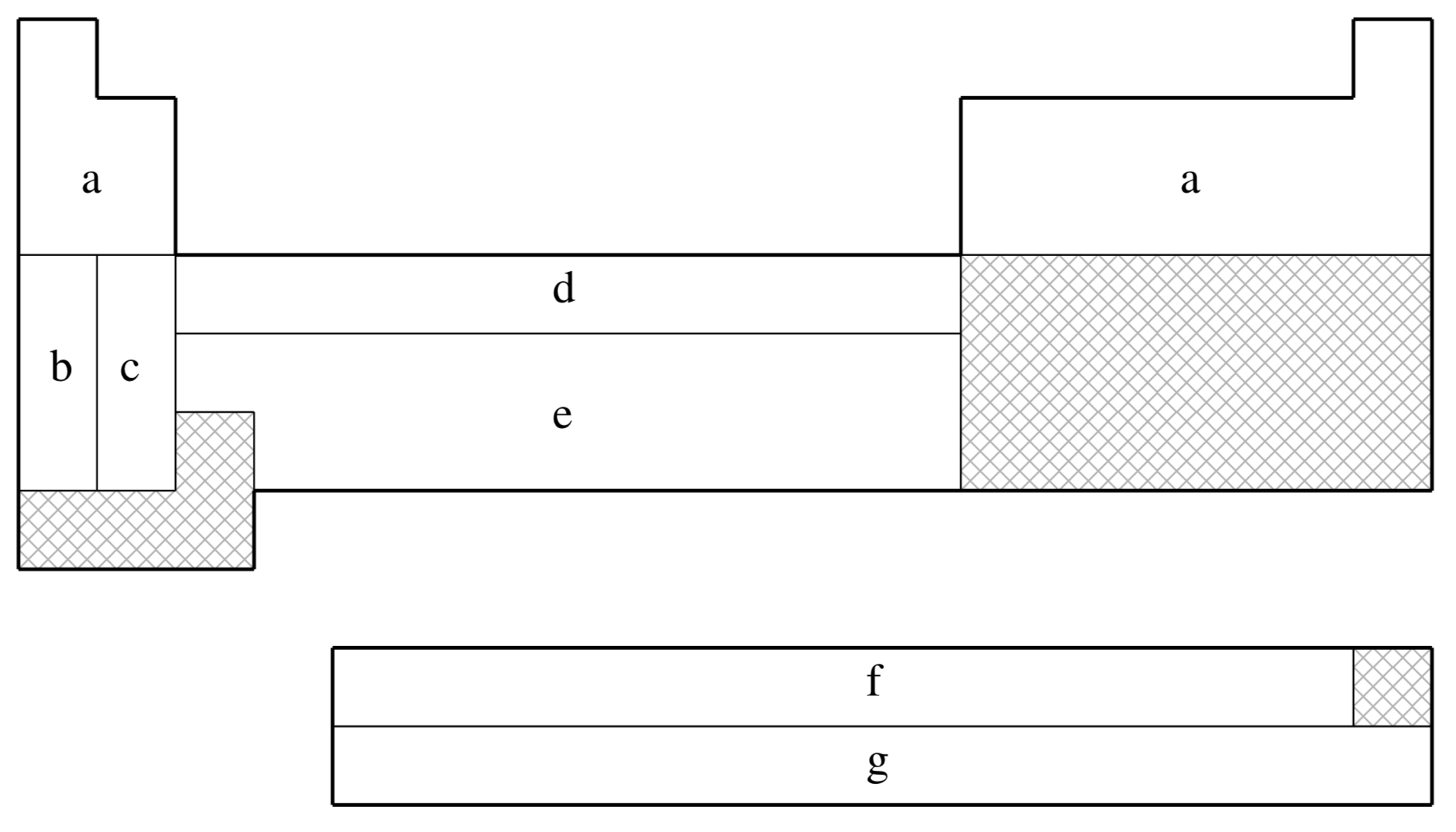
SRLC is not available for shaded elements
| (a) | No ECP; Pople 6-31G basis used |
|---|---|
| (b) | Fuentealba, Preuss, Stoll, & von Szentpály (Ref.
401
Chem. Phys. Lett. (1982), 89, pp. 418. Link ) |
| (c) | Fuentealba, von Szentpály, Preuss, & Stoll (Ref.
403
J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. (1985), 18, pp. 1287. Link ) |
| (d) | Bergner, Dolg, Küchle, Stoll, & Preuss (Ref.
112
Mol. Phys. (1993), 80, pp. 1431. Link ) |
| (e) | Nicklass, Dolg, Stoll, & Preuss, (Ref.
960
J. Chem. Phys. (1995), 102, pp. 8942. Link ) |
| (f) | Schautz, Flad, & Dolg (Ref.
1166
Theor. Chem. Acc. (1998), 99, pp. 231. Link ) |
| (g) | Fuentealba, Stoll, von Szentpály, Schwerdtfeger, & Preuss (Ref.
402
J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. (1983), 16, pp. L323. Link ) |
| (h) | von Szentpály, Fuentealba, Preuss, & Stoll (Ref.
1361
Chem. Phys. Lett. (1982), 93, pp. 555. Link ) |
| (i) | Küchle, Dolg, Stoll, & Preuss (Ref.
716
Mol. Phys. (1991), 74, pp. 1245. Link ) |
| (j) | Küchle (Ref. ) |
| Element | Core | Max Projector | Valence |
|---|---|---|---|
| H–He | none | none | (2s) |
| Li–Be | [He] | (2s,2p) | |
| B–N | [He] | (2s,2p) | |
| O–F | [He] | (2s,3p) | |
| Ne | [He] | (4s,4p,3d,1f) | |
| Na–P | [Ne] | (2s,2p) | |
| S–Cl | [Ne] | (2s,3p) | |
| Ar | [Ne] | (4s,4p,3d,1f) | |
| K–Ca | [Ar] | (2s,2p) | |
| Zn | [Ar]+3d | (3s,2p) | |
| Ga–As | [Ar]+3d | (2s,2p) | |
| Se–Br | [Ar]+3d | (2s,3p) | |
| Kr | [Ar]+3d | (4s,4p,3d,1f) | |
| Rb–Sr | [Kr] | (2s,2p) | |
| In–Sb | [Kr]+4d | (2s,2p) | |
| Te–I | [Kr]+4d | (2s,3p) | |
| Xe | [Kr]+4d | (4s,4p,3d,1f) | |
| Cs–Ba | [Xe] | (2s,2p) | |
| Hg–Bi | [Xe]+4f+5d | (2s,2p,1d) | |
| Po–At | [Xe]+4f+5d | (2s,3p,1d) | |
| Rn | [Xe]+4f+5d | (2s,2p,1d) | |
| Ac–Lr | [Xe]+4f+5d | (5s,5p,4d,3f,2g) |
SRSC is not available for shaded elements
| (a) | No ECP; Pople 6-311G basis used |
|---|---|
| (b) | Leininger, Nicklass, Küchle, Stoll, Dolg, & Bergner (Ref.
779
Chem. Phys. Lett. (1996), 255, pp. 274. Link ) |
| (c) | Kaupp, Schleyer, Stoll, & Preuss (Ref.
658
J. Chem. Phys. (1991), 94, pp. 1360. Link ) |
| (d) | Dolg, Wedig, Stoll, & Preuss (Ref.
340
J. Chem. Phys. (1987), 86, pp. 866. Link ) |
| (e) | Andrae, Häußermann, Dolg, Stoll, & Preuss (Ref.
47
Theor. Chem. Acc. (1990), 77, pp. 123. Link ) |
| (f) | Dolg, Stoll, & Preuss (Ref.
338
J. Chem. Phys. (1989), 90, pp. 1730. Link ) |
| (g) | Küchle, Dolg, Stoll, & Preuss (Ref.
717
J. Chem. Phys. (1994), 100, pp. 7535. Link ) |
| (h) | Dolg, Stoll, Preuss, & Pitzer (Ref.
339
J. Phys. Chem. (1993), 97, pp. 5852. Link ) |
| Element | Core | Max Projector | Valence |
|---|---|---|---|
| H–He | none | none | (3s) |
| Li–Ne | none | none | (4s,3p,1d) |
| Na–Ar | none | none | (6s,5p,1d) |
| K | [Ne] | (5s,4p) | |
| Ca | [Ne] | (4s,4p,2d) | |
| Sc–Zn | [Ne] | (6s,5p,3d) | |
| Rb | [Ar]+3d | (5s,4p) | |
| Sr | [Ar]+3d | (4s,4p,2d) | |
| Y–Cd | [Ar]+3d | (6s,5p,3d) | |
| Cs | [Kr]+4d | (5s,4p) | |
| Ba | [Kr]+4d | (3s,3p,2d,1f) | |
| Ce–Yb | [Ar]+3d | (5s,5p,4d,3f) | |
| Hf–Pt | [Kr]+4d+4f | (6s,5p,3d) | |
| Au | [Kr]+4d+4f | (7s,3p,4d) | |
| Hg | [Kr]+4d+4f | (6s,6p,4d) | |
| Ac–Lr | [Kr]+4d+4f | (8s,7p,6d,4f) |
For elements Rb–Rn, all the Karlsruhe “def2” basis sets are paired with a
common set of ECPs.
1385
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.
(2005),
7,
pp. 3297.
Link
It is briefly summarized in the table
below (the number of valence basis functions depend on the basis set in use,
so it is not presented):
| Element | Core | Max Projector |
|---|---|---|
| H–Kr | none | none |
| Rb–Xe | [Ar]+3d | |
| Cs–La | [Kr]+4d | |
| Hf–Rn | [Kr]+4d+4f |