5.12 Analytic Gradients and Properties for Coupled-Cluster Methods
Analytic gradients are available for CCSD, OO-CCD/VOD, CCD, and QCCD/VQCCD methods for both closed- and open-shell references (UHF and RHF only), including frozen core and/or virtual functionality. In addition, gradients for selected GVB models are available.
For the CCSD and OO-CCD wavefunctions, Q-Chem can also calculate dipole moments, 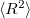 (as well as XX, YY and ZZ components separately, which is useful for assigning different Rydberg states, e.g.,
(as well as XX, YY and ZZ components separately, which is useful for assigning different Rydberg states, e.g., 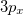 vs.
vs. 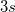 , etc.), and the
, etc.), and the 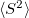 values. Interface of the CCSD and (V)OO-CCD codes with the NBO 5.0 package is also available. This code is closely related to EOM-CCSD properties/gradient calculations (Section 6.7.12). Solvent models available for CCSD are described in Chapter 11.2.
values. Interface of the CCSD and (V)OO-CCD codes with the NBO 5.0 package is also available. This code is closely related to EOM-CCSD properties/gradient calculations (Section 6.7.12). Solvent models available for CCSD are described in Chapter 11.2.
Limitations: Gradients and fully relaxed properties for ROHF and non-HF (e.g., B3LYP) orbitals as well as RI approximation are not yet available.
Note: If gradients or properties are computed with frozen core/virtual, the algorithm will replace frozen orbitals to restricted. This will not affect the energies, but will change the orbital numbering in the CCMAN printout.
5.12.1 Job Control Options
CC_REF_PROP
Whether or not the non-relaxed (expectation value) or full response (including orbital relaxation terms) one-particle CCSD properties will be calculated. The properties currently include permanent dipole moment, the second moments
,
, and
of electron density, and the total
(in atomic units). Incompatible with JOBTYPE=FORCE, OPT, FREQ.
TYPE:
LOGICAL
DEFAULT:
FALSE
(no one-particle properties will be calculated)
OPTIONS:
FALSE, TRUE
RECOMMENDATION:
Additional equations need to be solved (lambda CCSD equations) for properties with the cost approximately the same as CCSD equations. Use default if you do not need properties. The cost of the properties calculation itself is low. The CCSD one-particle density can be analyzed with NBO package by specifying NBO=TRUE, CC_REF_PROP=TRUE and JOBTYPE=FORCE.
CC_REF_PROP_TE
Request for calculation of non-relaxed two-particle CCSD properties. The two-particle properties currently include
. The one-particle properties also will be calculated, since the additional cost of the one-particle properties calculation is inferior compared to the cost of
. The variable CC_REF_PROP must be also set to TRUE.
TYPE:
LOGICAL
DEFAULT:
FALSE
(no two-particle properties will be calculated)
OPTIONS:
FALSE, TRUE
RECOMMENDATION:
The two-particle properties are computationally expensive, since they require calculation and use of the two-particle density matrix (the cost is approximately the same as the cost of an analytic gradient calculation). Do not request the two-particle properties unless you really need them.
CC_FULLRESPONSE
Fully relaxed properties (including orbital relaxation terms) will be computed. The variable CC_REF_PROP must be also set to TRUE.
TYPE:
LOGICAL
DEFAULT:
FALSE
(no orbital response will be calculated)
OPTIONS:
FALSE, TRUE
RECOMMENDATION:
Not available for non UHF/RHF references and for the methods that do not have analytic gradients (e.g., QCISD).
5.12.2 Examples
Example 5.102 CCSD geometry optimization of HHeF followed up by properties calculations
$molecule
0 1
H .000000 .000000 -1.886789
He .000000 .000000 -1.093834
F .000000 .000000 .333122
$end
$rem
JOBTYPE OPT
METHOD CCSD
BASIS aug-cc-pVDZ
GEOM_OPT_TOL_GRADIENT 1
GEOM_OPT_TOL_DISPLACEMENT 1
GEOM_OPT_TOL_ENERGY 1
$end
@@@
$molecule
READ
$end
$rem
JOBTYPE SP
METHOD CCSD
BASIS aug-cc-pVDZ
SCF_GUESS READ
CC_REF_PROP 1
CC_FULLRESPONSE 1
$end
Example 5.103 CCSD on 1,2-dichloroethane gauche conformation using SCRF solvent model
$molecule
0 1
C 0.6541334418569877 -0.3817051480045552 0.8808840579322241
C -0.6541334418569877 0.3817051480045552 0.8808840579322241
Cl 1.7322599856434779 0.0877596094659600 -0.4630557359272908
H 1.1862455146007043 -0.1665749506296433 1.7960750032785453
H 0.4889356972641761 -1.4444403797631731 0.8058465784063975
Cl -1.7322599856434779 -0.0877596094659600 -0.4630557359272908
H -1.1862455146007043 0.1665749506296433 1.7960750032785453
H -0.4889356972641761 1.4444403797631731 0.8058465784063975
$end
$rem
JOBTYPE SP
METHOD CCSD
BASIS 6-31g**
N_FROZEN_CORE FC
CC_SAVEAMPL 1 Save CC amplitudes on disk
SOLVENT_METHOD SCRF
SOL_ORDER 15 L=15 Multipole moment order
SOLUTE_RADIUS 36500 3.65 Angstrom Solute Radius
SOLVENT_DIELECTRIC 89300 8.93 Dielectric (Methylene Chloride)
$end