11.6 Density Embedding Scheme
The exact density embedding method adapted from the method of Manby, Miller, and co-workers [682] allows embedding calculations to extend beyond electrostatic embedding. This embedding scheme allows for the fragmentation of a system into two interacting subsystems, which can be treated at two different levels of quantum mechanics (QM/QM), for example coupled cluster embedded in DFT. This type of embedding fully accounts for polarization as well as quantum mechanical exchange, as calculated from the supermolecular embedding density and the exchange correlation functional used. The goal of this embedding theory is to perform, say, a DFT calculation on fragment 1 in the presence of fragment 2.
11.6.1 Theory
Conventional supermolecular KS-DFT calculations contain several non-additive terms consisting of kinetic energies and exchange-correlation effects. These non-additive terms are eliminated by applying a level-shift projection operator to maintain orthogonality between fragments when performing a 1-in-2 energy calculation.
The process begins by performing a KS-DFT calculation on the full system, or supermolecule. The KS-DFT calculation is then repeated for fragment 1-in-2, which is fragment 1 in the presence of the localized MOs of fragment 2 taken from the supermolecular full calculation. The Fock Matrix for this calculation is constructed as follows,
![\begin{equation} \label{eq:des_ fock} \mathbf{f}^{(1)} = \mathbf{h} + \mathbf{J}[\gamma ^{(1)} + \gamma ^{(2)}] - \nu _{xc}[\gamma ^{(1)} + \gamma ^{(2)}] + \mu \mathbf{P}^{(2)} \end{equation}](images/img-1764.png) |
(11.54) |
where P is the level-shift projection operator constructed as:
![\begin{equation} \label{eq:des_ proj} \mathbf{P}^{(2)}_{\alpha \beta } = [ \mathbf{S} \gamma ^{(2)} \mathbf{S} ]_{\alpha \beta } \end{equation}](images/img-1765.png) |
(11.55) |
where 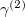 is the localized density of fragment 2, and S is the AO overlap matrix. Upon convergence, an energy correction term is added to the final energy to account for the level-shift projection operator contribution to the Fock Matrix energy. The correction term is calculated as the following:
is the localized density of fragment 2, and S is the AO overlap matrix. Upon convergence, an energy correction term is added to the final energy to account for the level-shift projection operator contribution to the Fock Matrix energy. The correction term is calculated as the following:
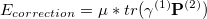 |
(11.56) |
Once the KS-DFT energy of fragment 1-in-2 is computed, a post KS method can be applied to this converged density to obtain the high-level QM additive energy of fragment 1. The same procedure can be repeated for fragment 2-in-1, without continuing to a post-DFT method to yield the low-level QM additive energy of the fragment 2. These energies are then summed to yield the total energy.
11.6.2 Job Control for Density Embedding Calculations
To use density embedding on a system, one must split the supermolecular system into two fragments indexed 1 and 2, and set EMBEDMAN to 1. This is done through the standard Q-Chem fragment input syntax. Two separate jobs must be run to find the total energy of fragment 1-in-2 at a high level QM theory, and fragment 2-in-1 at a low level QM theory. The order of the fragments in the $molecule section determines which fragment will undergo the high level QM. The user must submit a separate job for the 2-in-1 low-level QM calculation, with the order of the fragments reversed and EMBED_THEORY set to 0, which is the default value. The user must then add the final energies of the calculations to determine the total QM/QM embedded energy.
For the current Q-Chem implementation of density embedding, it is necessary to specify the basis as MIXED, which requires to define the basis for each individual atom. When using CCSD(T), one should specify ccman2 as TRUE, for Q-Chem’s most updated coupled-cluster code. The current implementation of density embedding only works in combination with the following settings: SCF_ALGORITHM = DIIS, INCFOCK = 0, and PURCAR = 222. It is also recommended that users disable symmetry for calculations with SYMMETRY = FALSE, and SYM_IGNORE = TRUE. Refer to the sample input for correct job settings.
EMBEDMAN
Turns density embedding on.
TYPE:
INTEGER
DEFAULT:
0
OPTIONS:
0
Do not use density embedding.
1
Turn on density embedding.
RECOMMENDATION:
Use EMBEDMAN for QM/QM density embedded calculations.
EMBED_THEORY
Specifies post-DFT method performed on fragment one.
TYPE:
INTEGER
DEFAULT:
0
OPTIONS:
0
No post HF method, only DFT on fragment one.
1
Perform CCSD(T) calculation on fragment one.
2
Perform MP2 calculation on fragment one.
RECOMMENDATION:
This should be 1 or 2 for the high-level QM calculation of fragment 1-in-2, and 0 for fragment 2-in-1 low-level QM calculation.
EMBED_MU
Specifies exponent value of projection operator scaling factor,
[Eq. eq:des_fock and eq:des_corr].
TYPE:
INTEGER
DEFAULT:
7
OPTIONS:
n
.
RECOMMENDATION:
Values of 2 - 7 are recommended. A higher value of
leads to better orthogonality of the fragment MOs. but
introduces numerical noise.
results in non-additive terms becoming too large. Energy corrections are fairly insensitive to changes in
within the range of
.
EMBED_THRESH
Specifies threshold cutoff for AO contribution used to determine which MOs belong to which fragments
TYPE:
INTEGER
DEFAULT:
500
OPTIONS:
n
Threshold
RECOMMENDATION:
Acceptable values range from 0 to 1000. Should only need to be tuned for non-highly localized MOs
Example 11.262 Input for a CCSD(T)/PBE density embedding calculation of He-in-HF. The sum of the final energies for these two jobs will yield the total QM/QM energy.
$molecule
0 1
--
0 1
He -4.63032 2.10289 -1.62399
--
0 1
F -8.00612 1.74605 -1.25581
H -7.40964 1.84462 -0.47756
$end
$rem
JOBTYPE SP
EXCHANGE PBE
CORRELATION PBE
BASIS mixed ! Must specify basis sets per atom in $basis section below
PURCAR 222
MAXSCF 100
SCF_ALGORITHM DIIS
INCFOCK 0
SYMMETRY false
SYM_IGNORE true
CC_SYMMETRY false
CCMAN2 true
EMBEDMAN 1 ! Turning density embedding on
EMBED_THEORY 1 ! Running CCSD(T) on fragment 1 in 2, or He in FH
EMBED_MU 7 ! Default value
EMBED_THRESH 500 ! Default value for assigning MOs to fragments
$end
$basis
he 1
6-31G
****
f 2
6-31G
****
h 3
6-31G
****
$end
@@@
$molecule
0 1
--
0 1
F -8.00612 1.74605 -1.25581
H -7.40964 1.84462 -0.47756
--
0 1
He -4.63032 2.10289 -1.62399
$end
$rem
JOBTYPE SP
EXCHANGE PBE
CORRELATION PBE
BASIS mixed
PURCAR 222
MAXSCF 100
SCF_ALGORITHM DIIS
INCFOCK 0
SYMMETRY false
SYM_IGNORE true
EMBEDMAN 1
EMBED_THEORY 0 ! There will be no post-DFT calculations for HF-in-He
$end
$basis
f 1
6-31G
****
h 2
6-31G
****
he 3
6-31G
****
$end